
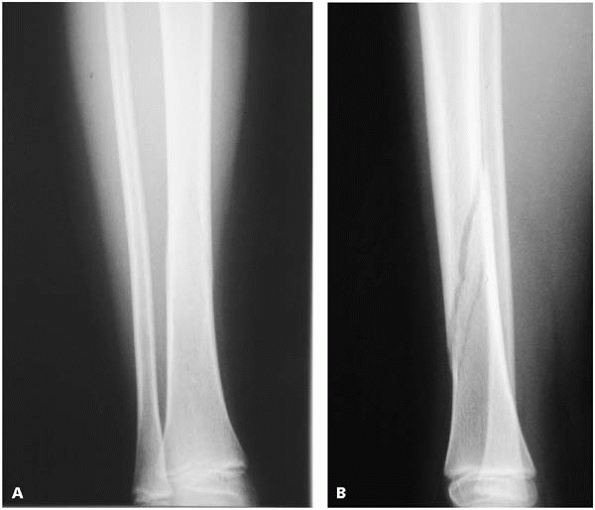
Stimulation of the tibial physis without a corresponding stimulation of Taylor 146īelieved that the valgus deformity was secondary to postfracture Injured at the time of the initial fracture (Salter-Harris type V 81īelieved that the lateral aspect of the proximal tibial physis was 135, 154 Lehner and Dubas 92 suggested that an expanding medial callus produced a valgus deformity, whereas Goff 46 and Keret et al. Reduction or the loss of satisfactory reduction in the weeks following In some cases, proximal tibia valga can be the result of an inadequate Many theories have been proposed to explain the development of a valgus deformity after a proximal tibial metaphyseal fracture ( Table 25-3). Literature however, it would seem certain that the current average Have been no updates of this information in the recent English With fractures of the tibia and fibula, followed by humeral, femoral,ġ994 report, the average Injury Severity Score of a child with a tibialįracture was 10 (range, 0 to 45) with an average hospital stay of 6.5 Concomitantįractures of the ankle and foot are the most common injuries associated Nine percent of pediatric tibial fractures are open. Approximately 16% to 26% of all abused children with a The tibia is the second most commonly fractured bone in abusedĬhildren. Most isolated fibular fractures result from a direct More than 50% of ipsilateral tibial and fibular fractures result from In children 1 to 4 years of age, whereas most tibial fractures inĬhildren 4 to 14 years of age are the result of sporting or traffic Tibial fractures due to bicycle spoke injuries occur almost exclusively

That present without an associated fibular fracture. Most tibial fractures in older children and Spiral or short oblique fractures in the distal and the middle one Tibial fractures in children under 4 years of age usually are isolated Thirty-five percent of pediatric tibial fractures are oblique, 32%Ĭomminuted, 20% transverse, and 13% spiral.

Tibia is the proximal third, yet these may be the most problematic. The least commonly affected portion of the 18, 142, 151įifty to 70% of tibial fractures occur in the distal third, and 19% toģ9% in the middle third. Ipsilateral fibular fractures occur with 30% of tibial fractures. Seventy percent of pediatric tibial fractures are isolated injuries 79 The average age of occurrence is 8 years, and the frequency of occurrence does not change significantly with age. 133, 142 The prevalence of tibial fractures in both boys and girls has increased since 1950. Pediatric long bone injuries (15%) after radial/ulnar and femoralįractures. Tibial and fibular fractures are the third most common


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
